NASA’s Kepler Space Telescope discovered an Earth-like planet circling a nearby star within the Goldilocks zone of our galaxy. Kepler-186f is around 500 light-years from Earth in the Cygnus constellation. The habitable zone, also identified as the Goldilocks zone, is the area around a star within which planetary-mass objects with enough atmospheric pressure can sustain liquid water at their surfaces.

While it has been projected that there are at least 40 billion Earth-sized planets circling in our Milky Way Galaxy, this specific finding is labelled the first Earth-sized planet to be discovered in the habitable zone of another star.
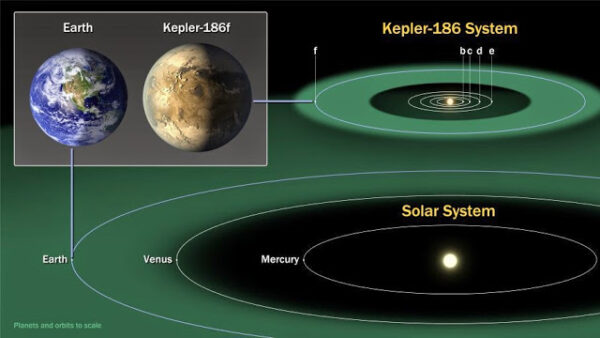
In addition to Kepler-186f, there are 4 other planets that circle a nearby star within the Kepler-186f system. What this means is that if the neighbouring star to this planet is just like our Sun, then the likelihood of life on this planet exponentially increases.
“We know of only one planet where life survives – Earth. When we hunt for life outside our solar system, we emphasis on discovering planets with features that mimic that of Earth,” said Elisa Quintana, research scientist at the SETI Institute at NASA’s Ames Research Center in Moffett Field, Calif., and lead author of the paper published in the journal Science. “Discovering a habitable zone planet similar to Earth in size is a major breakthrough.”
The neighboring star to Kepler-186f has half the mass and size as our solar system’s Sun and only gets one-third of the energy that we get from our Sun. Kepler-186f circles its star once every 130 days








 Photographer Finds Locations Of 1960s Postcards To See How They Look Today, And The Difference Is Unbelievable
Photographer Finds Locations Of 1960s Postcards To See How They Look Today, And The Difference Is Unbelievable  Hij zet 3 IKEA kastjes tegen elkaar aan en maakt dit voor zijn vrouw…Wat een gaaf resultaat!!
Hij zet 3 IKEA kastjes tegen elkaar aan en maakt dit voor zijn vrouw…Wat een gaaf resultaat!!  Scientists Discover 512-Year-Old Shark, Which Would Be The Oldest Living Vertebrate On The Planet
Scientists Discover 512-Year-Old Shark, Which Would Be The Oldest Living Vertebrate On The Planet  Hus til salg er kun 22 kvadratmeter – men vent til du ser det indvendigt
Hus til salg er kun 22 kvadratmeter – men vent til du ser det indvendigt  Superknepet – så blir snuskiga ugnsformen som ny igen!
Superknepet – så blir snuskiga ugnsformen som ny igen!  Meteorite That Recently Fell in Somalia Turns Out to Contain Two Minerals Never Before Seen on Earth
Meteorite That Recently Fell in Somalia Turns Out to Contain Two Minerals Never Before Seen on Earth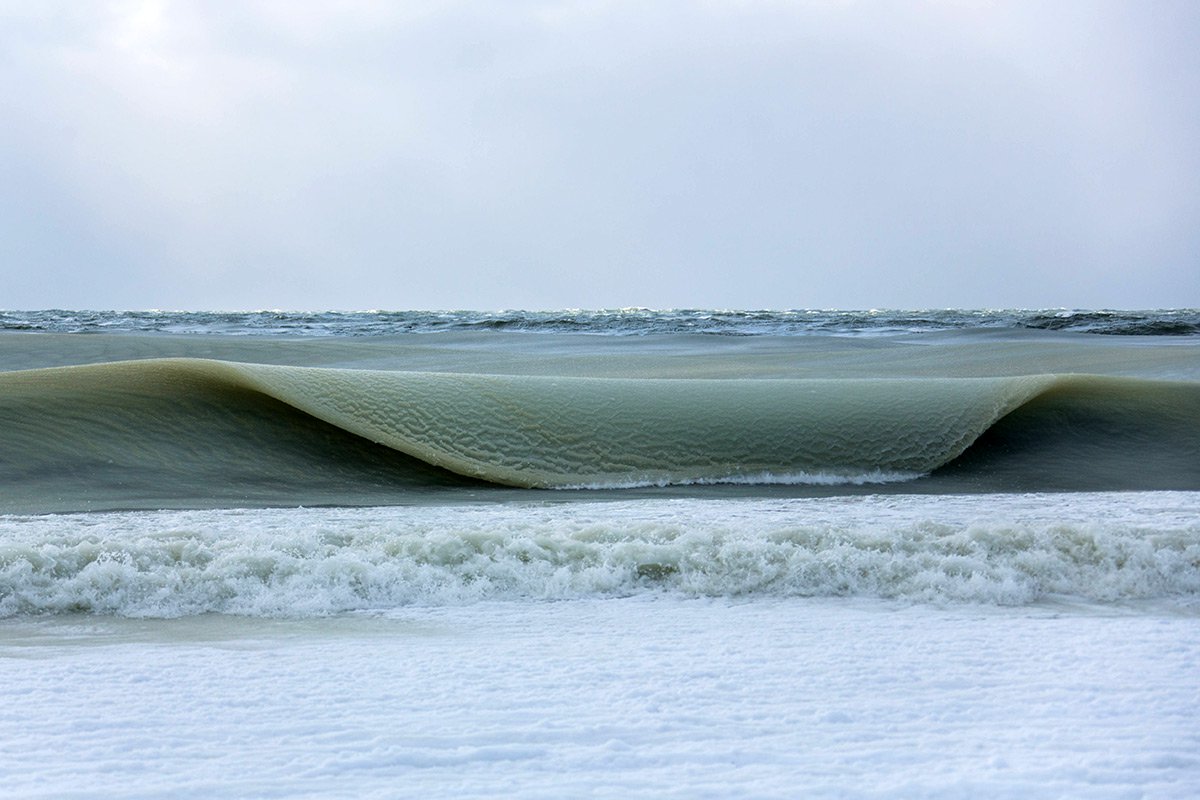  Nearly Frozen Waves Captured On Camera By Nantucket Photographer
Nearly Frozen Waves Captured On Camera By Nantucket Photographer  It’s Official: Astronomers Have Discovered another Earth
It’s Official: Astronomers Have Discovered another Earth 